导航
通过工作流串联训练与评测任务
最近更新时间:2023.07.07 14:56:27首次发布时间:2023.07.07 14:56:27
概述
机器学习平台工作流模块支持用户编排多个自定义任务。用户可以使用工作流串联模型训练与模型评估任务,并为每个任务提供不同的计算规格,在一次工作流任务中灵活完成训练与评估任务。
本文介绍一个简单的训练+评估工作流demo。该工作流使用PytorchDDP框架拉起一个多机GPU训练任务,并在训练结束将模型文件存储到TOS。然后拉起一个单机CPU任务,读取训练好的模型文件,在测试数据集上进行模型效果的评估。
开发训练与评估代码
假设用户已在开发机或本地电脑内编写好模型的训练与评估代码。如下是一个在CIFAR数据集中进行图像分类的模型训练与评估代码例子,用于下文功能演示。
import argparse import torch import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transforms import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.distributed as dist import torch.optim as optim transform = transforms.Compose( [transforms.ToTensor(), transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))]) batch_size = 4 classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck') class Net(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5) self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120) self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84) self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10) def forward(self, x): x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x))) x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x))) x = torch.flatten(x, 1) # flatten all dimensions except batch x = F.relu(self.fc1(x)) x = F.relu(self.fc2(x)) x = self.fc3(x) return x def train(trainloader, epochs, save_path, device): print('Running Training') net = Net() net.to(device) criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9) for epoch in range(epochs): # loop over the dataset multiple times running_loss = 0.0 for i, data in enumerate(trainloader, 0): # get the inputs; data is a list of [inputs, labels] inputs, labels = data inputs, labels = inputs.to(device), labels.to(device) # zero the parameter gradients optimizer.zero_grad() # forward + backward + optimize outputs = net(inputs) loss = criterion(outputs, labels) loss.backward() optimizer.step() # print statistics running_loss += loss.item() if i % 2000 == 1999: # print every 2000 mini-batches print(f'[{epoch + 1}, {i + 1:5d}] loss: {running_loss / 2000:.3f}') running_loss = 0.0 print('Finished Training') torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path) print('Model Saved') def test(testloader, model_path, device): print('Running Testing') dataiter = iter(testloader) images, labels = next(dataiter) net = Net() net.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device)) net.to(device) correct = 0 total = 0 # since we're not training, we don't need to calculate the gradients for our outputs with torch.no_grad(): for data in testloader: images, labels = data images, labels = images.to(device), labels.to(device) # calculate outputs by running images through the network outputs = net(images) # the class with the highest energy is what we choose as prediction _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1) total += labels.size(0) correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item() print(f'Accuracy of the network on the 10000 test images: {100 * correct // total} %') def main(): parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="PyTorch MNIST Example") parser.add_argument( "--epochs", type=int, default=10, metavar="N", help="number of epochs to train (default: 10)", ) parser.add_argument( "--model_path", type=str, help="model path", required=True, ) parser.add_argument( "--data_path", type=str, help="data path", required=True, ) parser.add_argument( "--train", action="store_true", default=False, help="run train func if true", ) parser.add_argument( "--test", action="store_true", default=False, help="run test func if true", ) parser.add_argument("--local-rank", default=-1, type=int) args = parser.parse_args() device = torch.device('cuda:0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu') print(f"use device={device}, local_rank={args.local_rank}") if args.local_rank >= 0: torch.cuda.set_device(args.local_rank) dist.init_process_group(backend="nccl") if args.train: trainset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=args.data_path, train=True, download=False, transform=transform) trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, num_workers=2) train(trainloader, args.epochs, args.model_path, device) elif args.test: testset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=args.data_path, train=False, download=False, transform=transform) testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=2) test(testloader, args.model_path, device) else: print("Either train or test flag must be set") exit(1) if __name__ == "__main__": main()
定义工作流
目前用户需使用YAML定义工作流任务。如下是一个串联了训练与评估任务的工作流demo。
该工作流拥有三个工作流运行输入,分别是队列名,生成的模型文件名,与训练次数epochs。其中训练次数epochs指定了默认值2。
该工作流拥定义了2个自定义任务模板。
train_task_template拉起2两台单卡V100计算节点,挂载了TOS到任务容器内,上传本地训练代码文件到容器内,使用pytorch进行分布式训练后,将模型文件保存回TOS。evaluate_task_template拉起一台CPU规格计算节点,同样挂载了TOS到任务容器内,上传本地评估代码到容器内,对训练任务生成的模型文件进行评估。该工作流串联了以上两个自定义任务,定义了任务间的依赖关系,并为每个任务指定了输入参数的值。
version: v1 kind: PipelineTemplate inputs: - name: queue type: string hint: 队列名 - name: model_name type: string hint: 模型文件名 - name: epochs type: int hint: train epochs default_value: 2 task_templates: - name: train_task_template type: CustomTask inputs: - name: queue type: string hint: 队列名 - name: model_name type: string hint: 模型文件名 - name: epochs type: int hint: train epochs spec: Entrypoint: | python -m torch.distributed.launch \ --nproc_per_node $MLP_WORKER_GPU \ --master_addr $MLP_WORKER_0_HOST \ --node_rank $MLP_ROLE_INDEX \ --master_port $MLP_WORKER_0_PORT \ --nnodes $MLP_WORKER_NUM \ /root/code/code.py \ --epochs {{inputs.epochs}} \ --model_path /data/model/{{inputs.model_name}} \ --data_path /data/cifar-10-python/ \ --train Framework: PyTorchDDP UserCodePath: samples/pipeline/code/cifar_training_and_evaluation_demo/code.py RemoteMountCodePath: /root/code ImageUrl: vemlp-cn-beijing.cr.volces.com/preset-images/pytorch:2.0.0 ResourceQueueName: '{{inputs.queue}}' Storages: - Type: "Tos" MountPath: "/data" # 容器中的挂载目录 Bucket: "pipeline-demo" # 待挂载的 TOS Bucket Prefix: "/" # 待挂载的 TOS Bucket 下的目录路径 TaskRoleSpecs: - Flavor: ml.g1v.2xlarge RoleName: worker RoleReplicas: 2 - name: evaluate_task_template type: CustomTask inputs: - name: queue type: string hint: 队列信息 - name: model_name type: string hint: 模型文件名 spec: Entrypoint: | python /root/code/code.py \ --model_path /data/model/{{inputs.model_name}} \ --data_path /data/cifar-10-python/ \ --test Framework: Custom ImageUrl: vemlp-cn-beijing.cr.volces.com/preset-images/pytorch:2.0.0 ResourceQueueName: '{{inputs.queue}}' UserCodePath: samples/pipeline/code/cifar_training_and_evaluation_demo/code.py RemoteMountCodePath: /root/code Storages: - Type: "Tos" MountPath: "/data" # 容器中的挂载目录 Bucket: "pipeline-demo" # 待挂载的 TOS Bucket Prefix: "/" # 待挂载的 TOS Bucket 下的目录路径 TaskRoleSpecs: - Flavor: ml.g1ie.4xlarge RoleName: worker RoleReplicas: 1 tasks: - name: train_task task_template_name: train_task_template inputs: - name: queue value: '{{pipeline.inputs.queue}}' - name: model_name value: '{{pipeline.inputs.model_name}}' - name: epochs value: '{{pipeline.inputs.epochs}}' - name: evaluate_task task_template_name: evaluate_task_template inputs: - name: queue value: '{{pipeline.inputs.queue}}' - name: model_name value: '{{pipeline.inputs.model_name}}' dependencies: - train_task
运行工作流
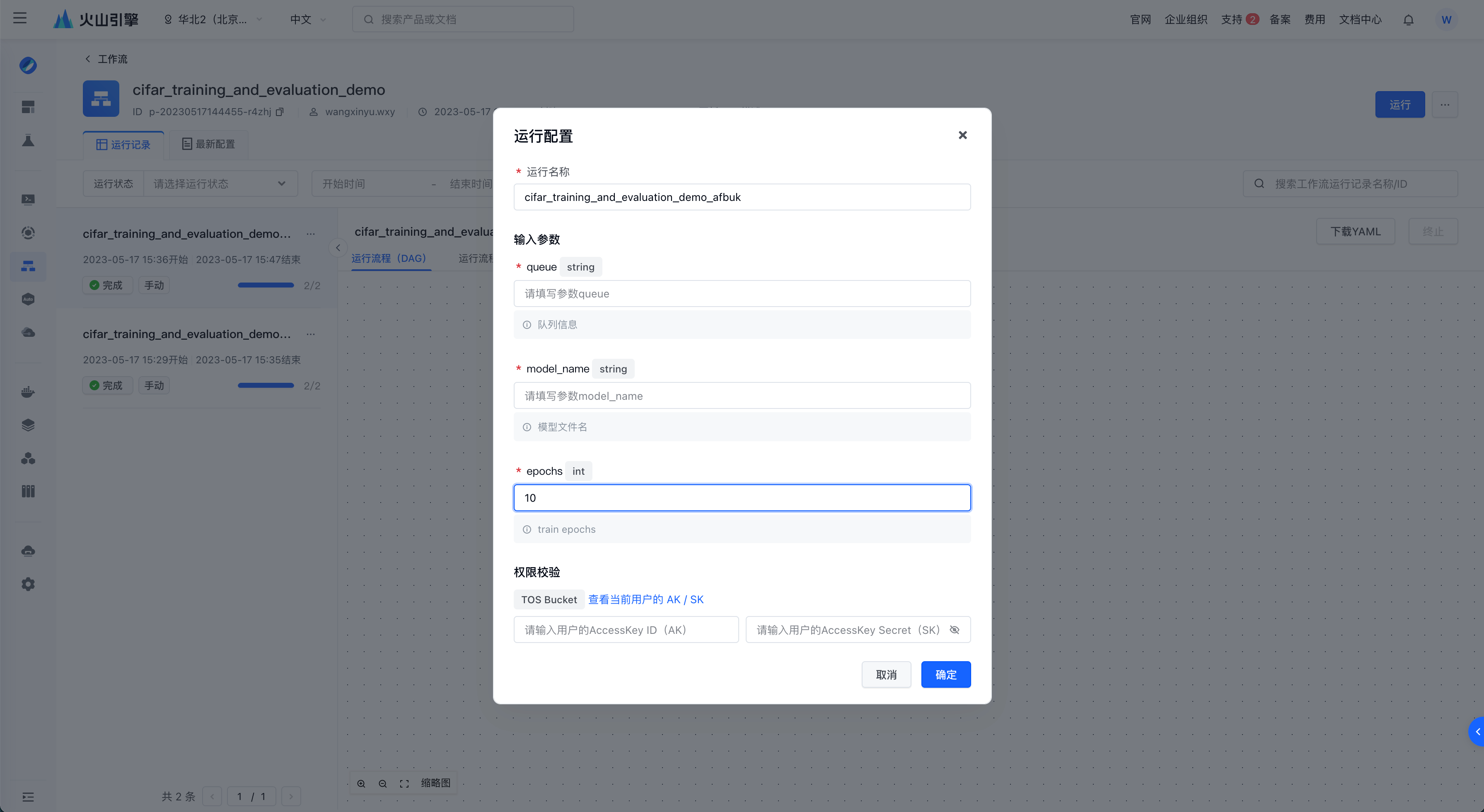
用户可以在控制台创建并运行工作流,在提交工作流后可在前端追踪工作流的运行信息。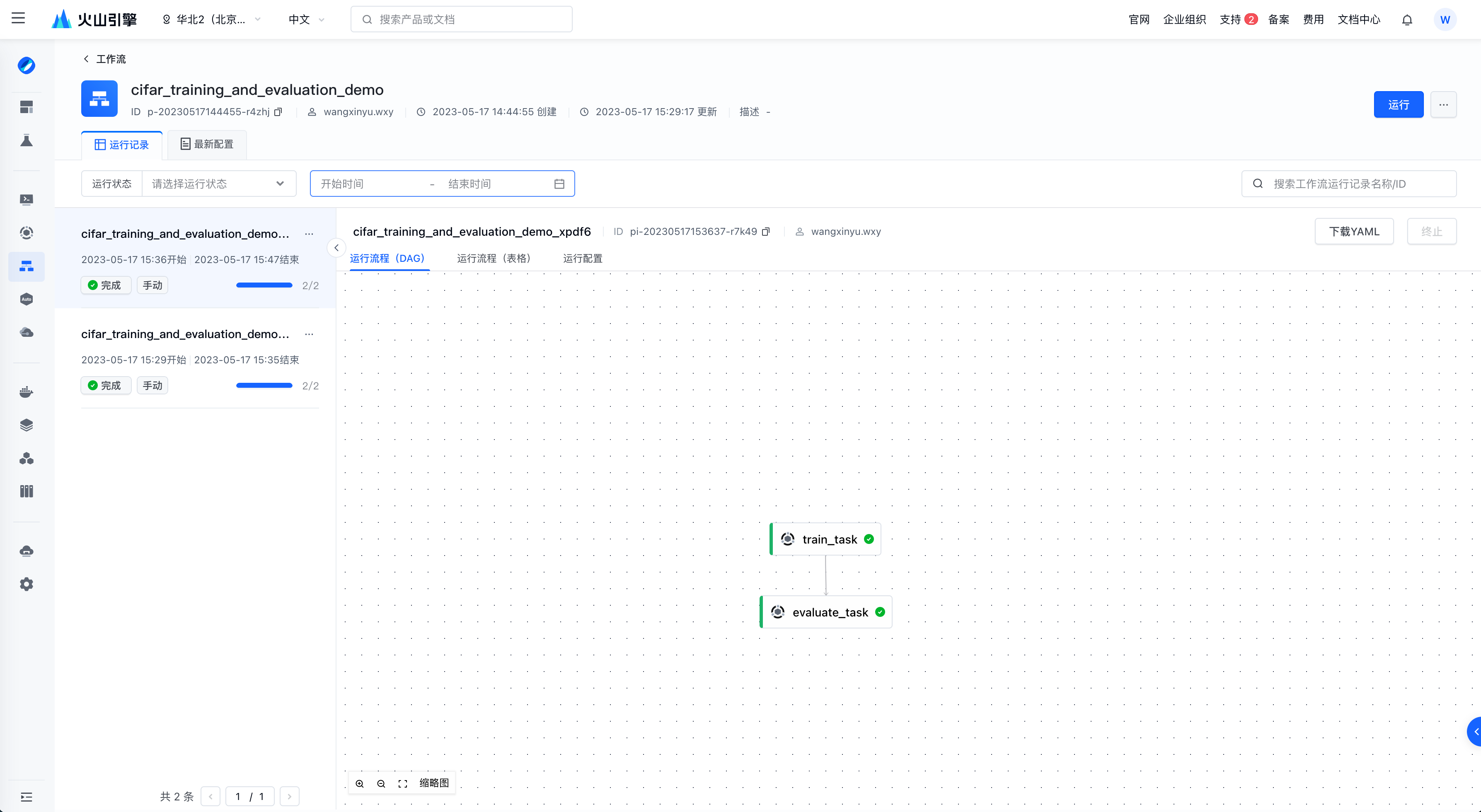
点击任务节点的任务详情可以跳转自定义任务详情页。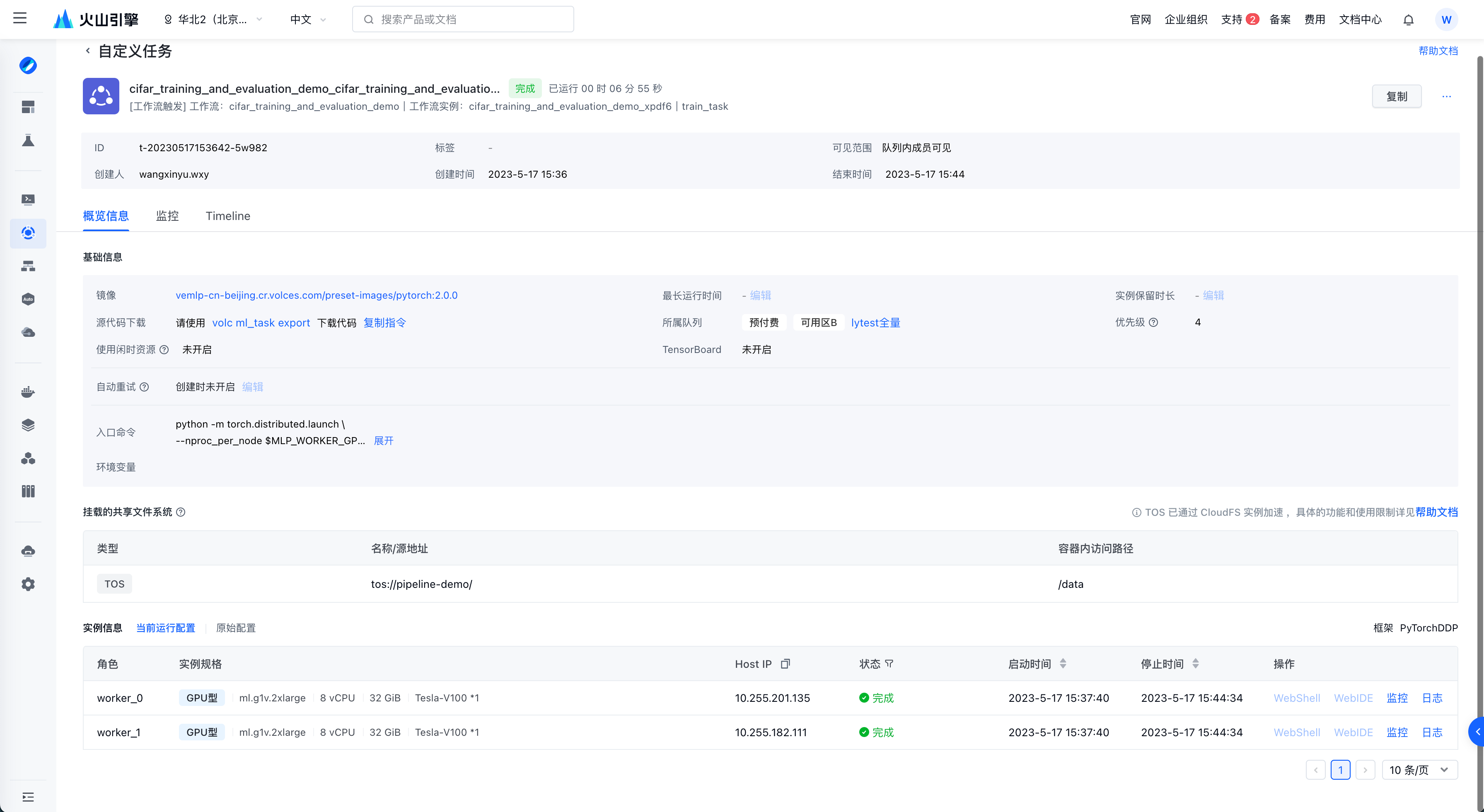
点击任务节点的日志可以跳转日志页面,查看训练与评估结果。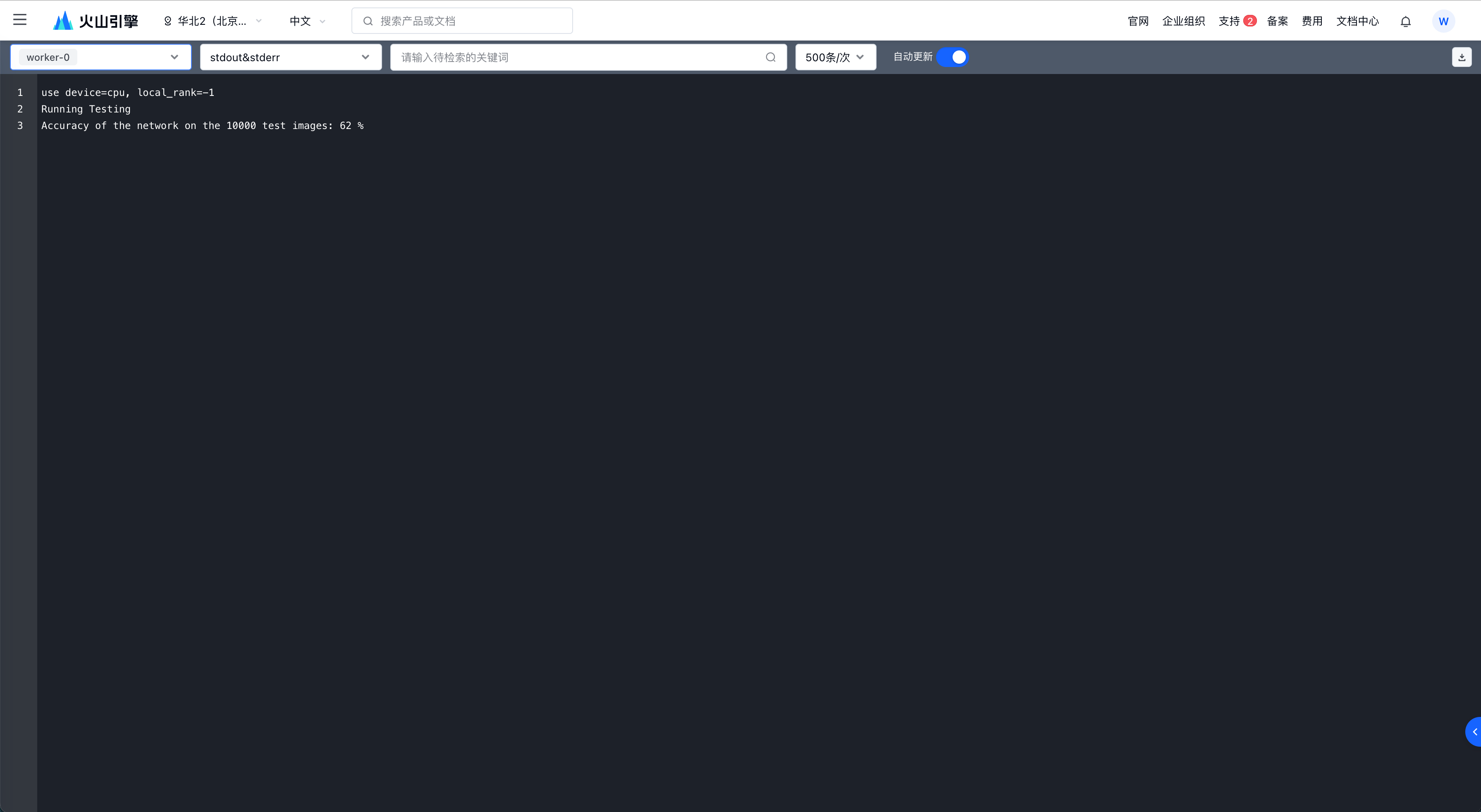
工作流创建后,用户可以在工作流详情页直接运行。